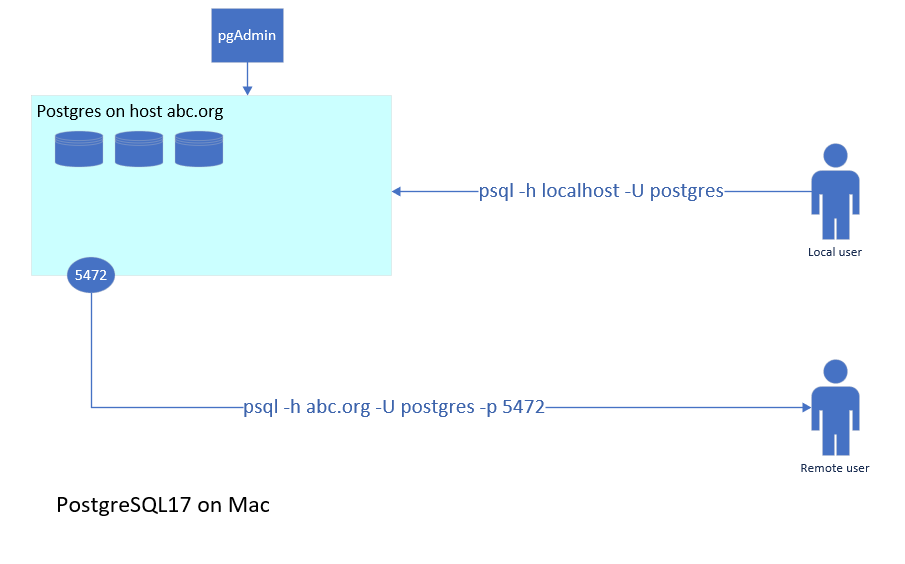
This information is directed at beginning users and was created for a student. The following section shows a scenario that applies to PostreSQL17 installed on a mac.
Sample CLI Database Creation
Place the following SQL commands in a file named setup.sql
-- SQL commands in setup.sql
-- Create a new database
CREATE DATABASE mydb;
-- Connect to the new database
\connect mydb
-- Create a table
CREATE TABLE employees (
id SERIAL PRIMARY KEY,
first_name VARCHAR(50),
last_name VARCHAR(50),
email VARCHAR(100),
hire_date DATE
);
-- Insert some sample data
INSERT INTO employees (first_name, last_name, email, hire_date) VALUES
('John', 'Doe', 'john.doe@example.com', '2023-01-15'),
('Jane', 'Smith', 'jane.smith@example.com', '2023-02-10'),
('Alice', 'Johnson', 'alice.johnson@example.com', '2023-03-20');
-- Create another table
CREATE TABLE departments (
dept_id SERIAL PRIMARY KEY,
dept_name VARCHAR(100)
);
-- Insert data into the departments table
INSERT INTO departments (dept_name) VALUES
('Human Resources'),
('Engineering'),
('Marketing');
Then run the following command.
psql -h localhost -p 5432 -U postgres -f setup.sql- Connect with psql
- select * from employees;
Commands
- \l # list databases
- \c <database> # connect to a database
- \d <table> # describe a table
- \d+ <table-name> # more information about a table
- \dt # display tables
- \dn # list all database schemas
- \du # list users and their roles
- \du <user> # retrieve a specific user
- \df # list all functions
- \q # quit postgres
